Elbow bursitis, also called olecranon bursitis, is swelling in the sac of fluid at the back of the elbow. It often presents as a soft lump but can sometimes be painful. So, what is a swollen bursa in the elbow, and how do we treat it?
What is the Olecranon bursa?
A bursa is a sac of fluid that forms over bony prominences such as the elbow and knee. Typically, the sac is thin and allows the movement of bony prominences, such as behind the elbow. However, this bursal sac in the elbow sometimes thickens with excess movement or pressure, forming elbow bursitis. The bursitis forms on the tip of the elbow, also known as the olecranon bursitis.
What are the symptoms of Olecranon bursitis?

The most common symptom of olecranon bursitis is swelling at the tip of the elbow. Sometimes, people report pain at the back of the elbow and restricted movement or stiffness. Direct pressure at the back of the elbow makes the pain worse. In addition, elbow bursitis can become infected in rare cases, also known as septic bursitis.
Bursitis can be caused by sudden trauma, such as a fall on the elbow, or it may pop up out of nowhere. Moreover, people who rest their elbows on hard surfaces, such as office workers, are likelier to develop a swollen bursal sac in the elbow. Infection may develop in elbow bursitis after a cut to the skin, allowing bugs to enter and grow. Certain diseases, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis, make it more likely to develop septic elbow bursitis.
How to diagnose a swollen bursa in the elbow?
Typically, people report swelling, pain, and stiffness at the back of the elbow. Other conditions cause pain and swelling, such as arthritis or tennis elbow. An X-ray is helpful to ensure the elbow joint is normal. We use an ultrasound or MRI scan if we are unsure of the diagnosis or think another cause exists.
Sometimes, a swollen bursa in the elbow is a sign of an underlying condition, such as inflammatory arthritis or gout. In these cases, other investigations, such as blood tests, are required.
Olecranon bursitis treatment
In most cases, simple treatments will settle the swelling and inflammation of a swollen bursa in the elbow. Ice and compression can help with swelling. Oral anti-inflammatory tablets such as ibuprofen can also help. Most importantly, people with elbow bursitis must understand that rest and ongoing inflammation prevention are critical to improving the condition.
Sometimes, a painful and swollen elbow bursa worsens despite simple treatments. In these cases, we could drain the fluid. Usually, a needle is placed in the bursal sac in the elbow, and the liquid is drained. The needle is directed under ultrasound to improve accuracy and prevent injury to other structures. Finally, we add a small dose of cortisone to prevent fluid reaccumulation.
Overall, we should be wary of invasive treatments for olecranon bursitis due to the increased risk of infection. We generally recommend avoiding drainage due to the risks involved, including the risk of introducing infection or developing a sinus tract. Instead, most cases will only need simple treatments.
Other frequently asked questions about olecranon bursitis:
How long does olecranon bursitis take to heal?
Most cases will settle with simple anti-inflammatory treatments such as ice, compression, and oral ibuprofen. Ususally, swelling resolves within a few months but can sometimes last longer. Also, it would be best to avoid direct pressure on the tip of the elbow, so elbow pads might help.
Is olecranon bursitis the same as tennis elbow?
No. Tennis elbow affects the tendon on the outside of the elbow. Generally, it causes pain but no swelling.
Can gout cause olecranon bursitis?
Yes. A high uric acid level can cause uric acid crystals to form in the olecranon bursa, causing bursitis. Other inflammatory arthritis diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also cause olecranon bursitis.
Does olecranon bursitis cause long-term damage to the elbow joint?
No. Olecranon bursitis is found outside the elbow joint. So, swelling in the bursa does not affect the health of the joint.

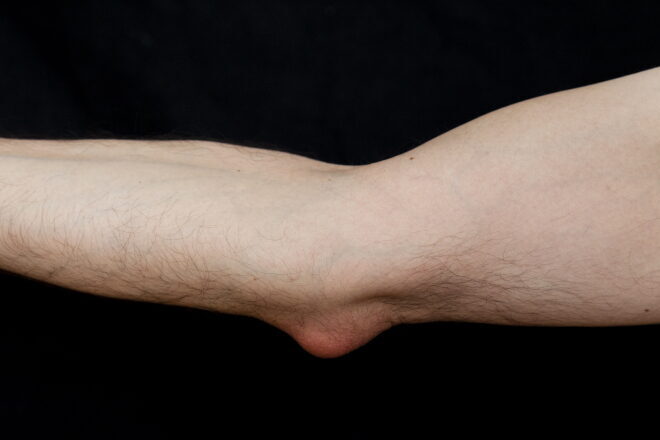

My lump is getting bigger and harder I have tried ibuprofen and ice but now it’s getting hard in places
I had elbow bursitis due to elbow trauma. There was no pain in elbow but it was swollen, so in 3 weeks after the trauma doctor drained liquid from the lump. However, in 3 days it was back same size as before.
Recurrence is common. I often advise compressing the elbow and continuing with ice packs even after drainage.
Regarding compression – what do you recommend? Just a tight wrap? On icing – how often?
I’ve had mine 3 weeks and nothing changing.
Hi John, I’d purchase something tight and stretchy, so it provides a moderate compression. Generally, I’d recommend ice at least twice a day 10-15 minutes at a time.
LM
Before it the bursitis developed I felt sharp pains in my elbow when I lift my bed ridden sister. 5 months later the lump developed. It is 6 months now. Can I use anti inflammatory drugs?
Hi – yes I’d still use inflammatory measures – ice, and topical and oral inflammatories
Mine started Nov 10th, after lifting weights. I didn’t realize what it was until about the 28th Nov when I continued lifting, but increased the weights… developed obvious bruising and pouch of fluid under the elbow (very similar to the picture above, except more purplish colored bruising). I was prescribed steroid and NSAD which i took for about a week. The swelling went down quite a bit after about 3 weeks, still sore at this time. I’ve had broken bones in the past and being 49 y/o I estimate this to continue another 2.5-3 months. Will probably look into making an appointment to get it checked out and maybe a cortisone shot to the area if necessary. Thanks for the extra info.
Hi Adam,
The same situation as yours, mine started 3 weeks before, and it continues to be swollen and is not painful unless I put pressure on it.
How did it progress and subside in your case?? were you able to lift weights again, how many days did you give it rest before starting all over again with lifting weights?
Bryan
both my elbows are affected and have large lumps very ugly
I developed Olecranon bursitis about 2 1/2 months ago. I’ve tried compression sleeves, but the pressure actually makes it worse. I’ve been taking NSAIDs and trying to avoid putting pressure on my elbow, but it doesn’t seem to be getting any better. My orthopaedist doesn’t recommend draining it and gave me an elbow pad but that doesn’t help. Any suggestions?
Thanks, Peter, for the question. Your orthopaedist is right to be wary. Injecting the bursae is not without risk, including infection (which can spread into the joint). Generally, most cases settle with anti-inflammatory measures, such as regular ice packs and avoiding direct pressure (even light pressure from a desk can be problematic). In persistent cases, I suggest an ultrasound to exclude co-existing triceps tendon pathology (such as calcification or tendonitis).
LM